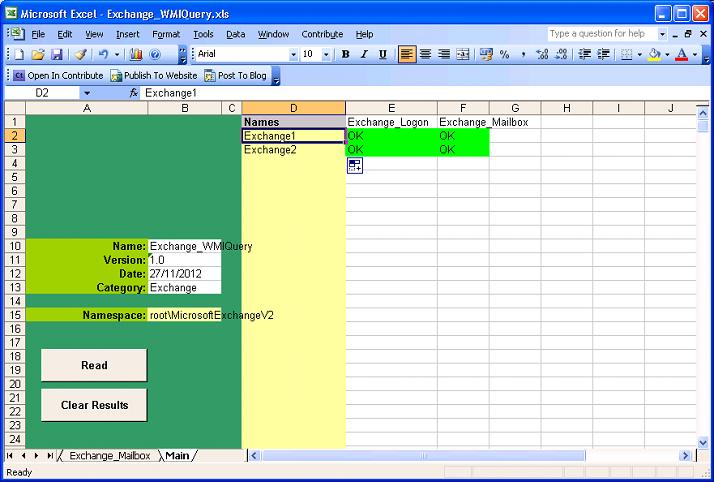
The Exchange_WMIQuery spreadsheet allows a list of Exchange Servers to have a WMI queries sequentially performed and the results collated into a single workbook.
The control buttons on the left hand side perform the following function:
|
Button |
Functionality |
|
Read |
Performs the WMI Query on the list of Exchange Servers in column D. The list will be processed sequentially starting at Cell D2 until an empty cell is found. |
|
Clear Results |
Deletes the results from column E and higher |
Populates a list of Exchange Servers in column D, the servers should be specified by Netbios name.
Populate the WMI classes to be queried in row1 starting at Cell E1.
Select the read button to start the query, for each Exchange Server specified in Column D the WMI class specified in row 1 will be performed.
The Namespace must be specified in Cell B15 there are 2 namespaces for Exchange:
- root\MicrosoftExchangeV2
- root\cimv2\applications\exchange
For each class query the spreadsheet will bind to the <computername> & WMI namespace and perform the query "Select * from <class>"
Where <computername> is the computer specified in column D and <class> is the WMI class specified in row1.
Each computer and classs queried will create a result in the cell corresponding to the row and column of the class and computer, the result will be colour coded as per the below table.
|
Result |
|
|
OK |
The computer and class has been queried successfully |
|
Not found |
The computer cannot be found |
|
Error |
There is an error querying the class or computer |
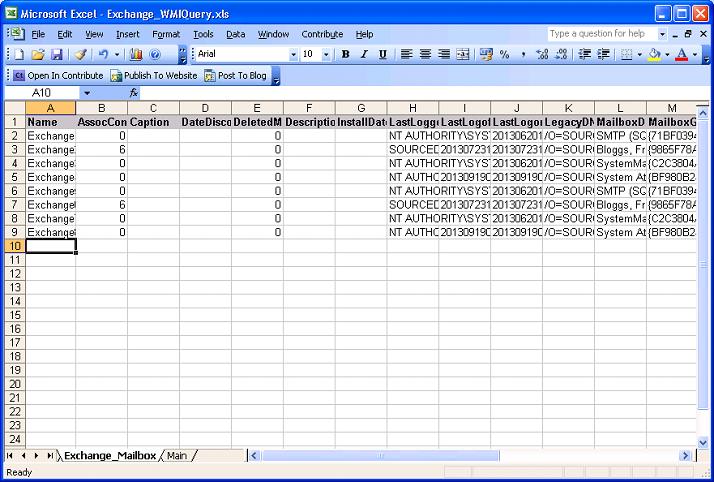
Each WMI class queried will generate a worksheet with the same name as the class, if the class name is more than 32 characters then the worksheet name will be truncated to 32 characters.
Within the WMI class worksheet, column A will contain the names of the computers queried and columns B and higher will contain the properties of the class.
The work sheet will be populated with the results from the WMI query and once completed standard excel sorting and filtering can be applied.
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Provides a standard interface that allows Microsoft scripting languages to manage windows computers.
Standard or elevated rights are required on the local computer to perform WMI queries depending on activity. On remote computers full administrative rights are required.
If there is a firewall between the local computer and the remote computers to be WMI queried then an exception must be created if not already.
Please view Microsoft Guidance on Windows Firewall (XP SP2 and higher) here:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa389286(v=vs.85).aspx
For more information on Exchange WMI classes and their usage then please view Microsoft Guidance here:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/exchange/ms876479(v=exchg.65).aspx
The below table lists Exchange classes:
|
Class |
|
root\MicrosoftExchangeV2 $1· |
|
Exchange_DSAccessDC |
|
Exchange_FolderTree |
|
Exchange_Link |
|
Exchange_Logon |
|
Exchange_Mailbox |
|
Exchange_MessageTrackingEntry |
|
Exchange_PublicFolder |
|
Exchange_Queue |
|
Exchange_QueueCacheReloadEvent |
|
Exchange_QueuedMessage |
|
Exchange_QueuedSMTPMessage |
|
Exchange_QueuedX400Message |
|
Exchange_QueueSMTPVirtualServer |
|
Exchange_QueueVirtualServer |
|
Exchange_QueueX400VirtualServer |
|
Exchange_ScheduleInterval |
|
Exchange_Server |
|
Exchange_SMTPLink |
|
Exchange_SMTPQueue |
|
Exchange_X400Link |
|
Exchange_X400Queue |
|
root\cimv2\applications\exchange |
|
ExchangeClusterResource |
|
ExchangeConnectorState |
|
ExchangeLink |
|
ExchangeQueue |
|
ExchangeServerState |
- Details
- Category: Exchange
- Published: 04 November 2013